4. Laparoendoscopic surgery
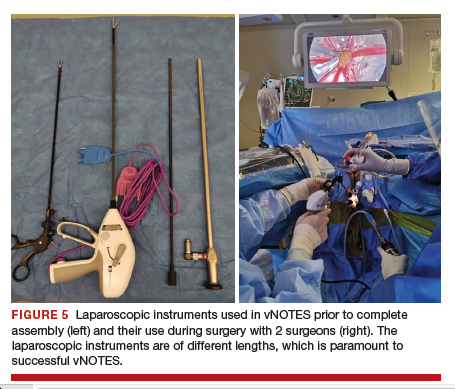
Instruments used in our surgeries include a 10-mm rigid 30° 43-cm working length laparoscope; a 44-cm LigaSure device (Medtronic); a 5-mm, 37-cm laparoscopic cobra grasping forceps and fenestrated grasper (Karl Storz); and a 5-mm, 45-cm laparoscopic suction with hydrodissection tip (Stryker) (FIGURE 5).
vNOTES allows a gynecologic surgeon the unique ability to survey the upper abdomen. The remainder of the surgery proceeds using basic laparoscopic single-site skills.
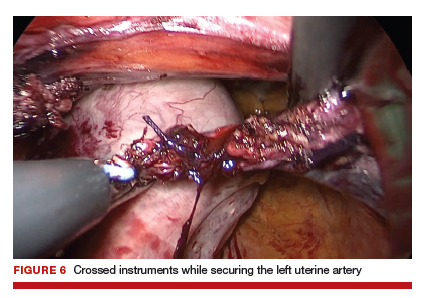
During vNOTES, as with all single-site surgical procedures, understanding the optimal placement of crossed instruments is important for successful completion. For example, when securing the right uterine artery, the surgeon needs to push the cervix toward the patient's left and slightly into the peritoneal cavity using a laparoscopic cobra grasper with his or her left hand while then securing the uterine pedicle using the LigaSure device with his or her right hand. This is then reversed when securing the left uterine artery, where the assistant surgeon pushes the cervix toward the patient's right while the surgeon secures the pedicle ("vaginal pull, laparoscopic push") (FIGURE 6).
This again is reiterated in securing the ovarian pedicles, which are pushed into the peritoneal cavity while being secured with the LigaSure device.
5. Specimen removal
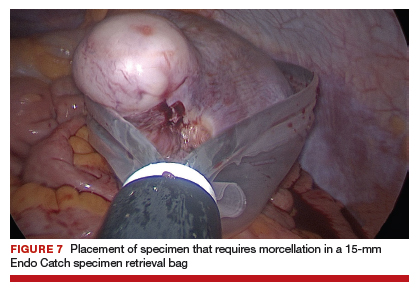
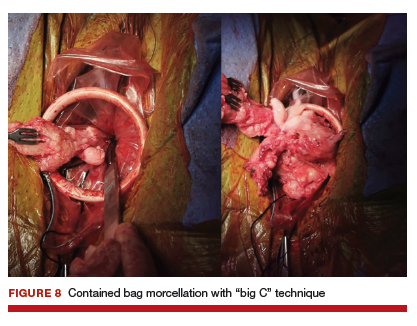
For large uteri or specimens that need morcellation, a 15-mm Endo Catch specimen retrieval bag (Medtronic) is introduced through the GelPOINT Mini system. The specimen is then placed in the bag and delivered to the vagina, where contained bag morcellation is performed in standard fashion (FIGURES 7 AND 8). We utilized the "big C" technique by first grasping the specimen with a penetrating clamp. The clamp is then held in our nondominant hand and a No. 10 blade scalpel is used to create a reverse c-incision, keeping one surface of the specimen intact. This is continued until the specimen can be completely delivered through the vagina.
Specimens that do not require morcellation can be grasped laparoscopically, brought to the GelPOINT Mini port, which is quickly disassembled, and delivered. The GelSeal cap is then reassembled.
6. Vaginal cuff closure
The colpotomy or vaginal cuff is closed with barbed suture continuously, as in traditional vaginal hysterectomy cuff closure. Uterosacral ligament suspension should be performed for vaginal cuff support.
vNOTES is the most recent innovative development in the field of minimally invasive surgery, and it has demonstrated feasibility and safety in the fields of general surgery, urology, and gynecology. Adopting vNOTES in clinical practice can improve patient satisfaction and cosmesis as well as surgical outcomes. Gynecologic surgeons can think of vNOTES hysterectomy as "placing an eye" in the vagina while performing transvaginal hysterectomy. The surgical principle of "vaginal pull, laparoscopic push" facilitates the learning process.