Scleromyxedema (SM) is a generalized papular and sclerodermoid form of lichen myxedematosus (LM), commonly referred to as papular mucinosis. It is a rare progressive disease of unknown etiology with systemic manifestations that cause serious morbidity and mortality. Diagnostic criteria were initially created by Montgomery and Underwood1 in 1953 and revised by Rongioletti and Rebora2 in 2001 as follows: (1) generalized papular and sclerodermoid eruption; (2) histologic triad of mucin deposition, fibroblast proliferation, and fibrosis; (3) monoclonal gammopathy; and (4) absence of thyroid disease. There are several reports of LM in association with hypothyroidism, most of which can be characterized as atypical.3-8 We present a case of SM in a patient with Hashimoto thyroiditis and propose that the presence of thyroid disease should not preclude the diagnosis of SM.
Case Report
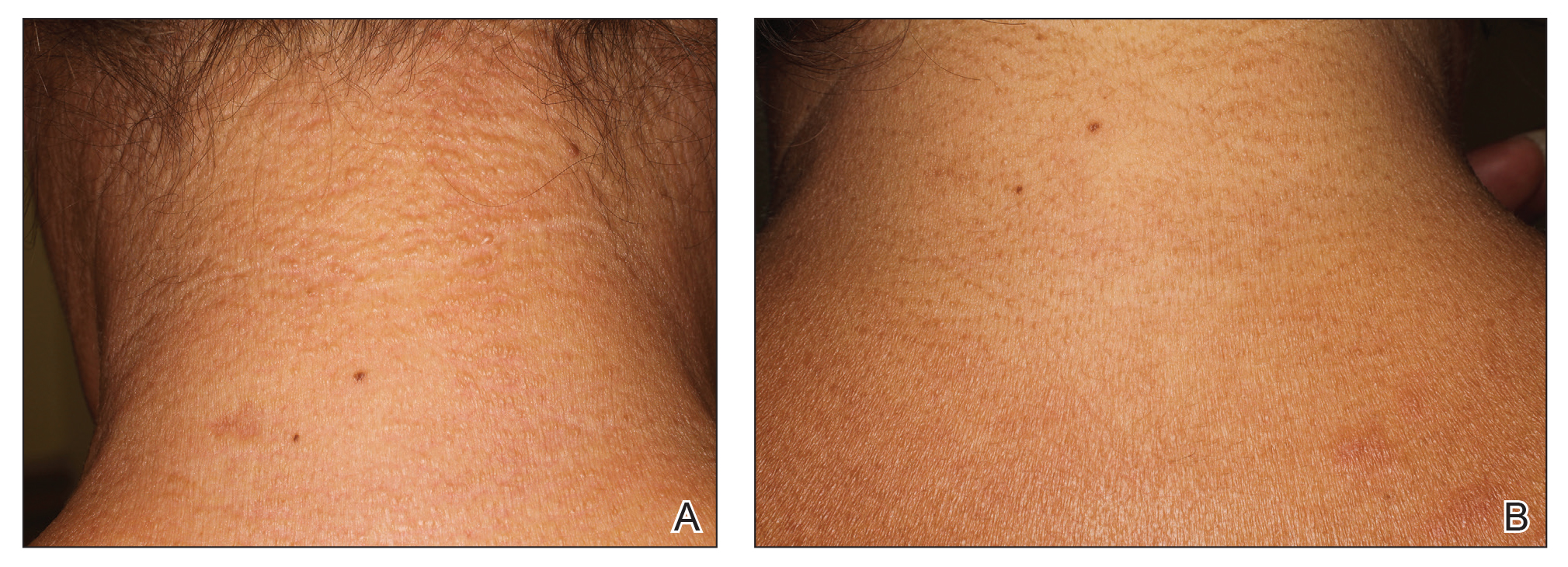
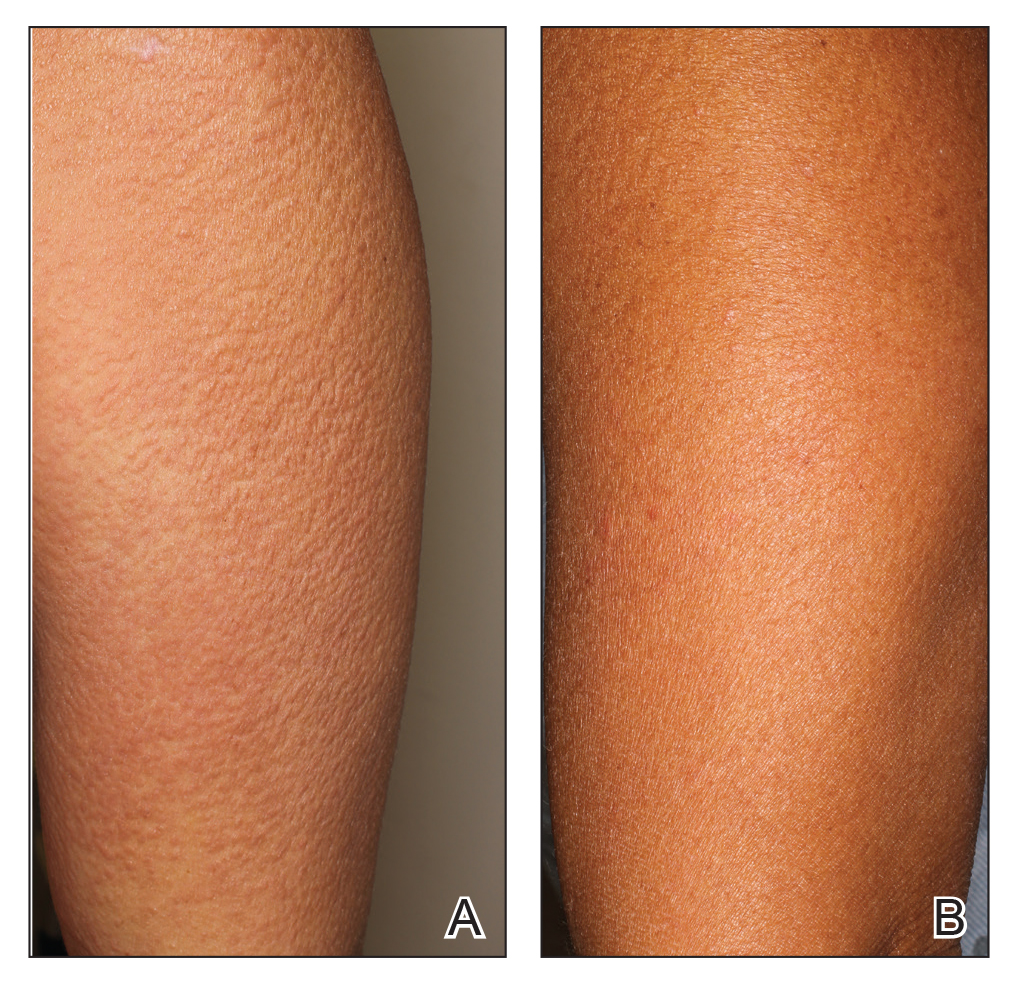
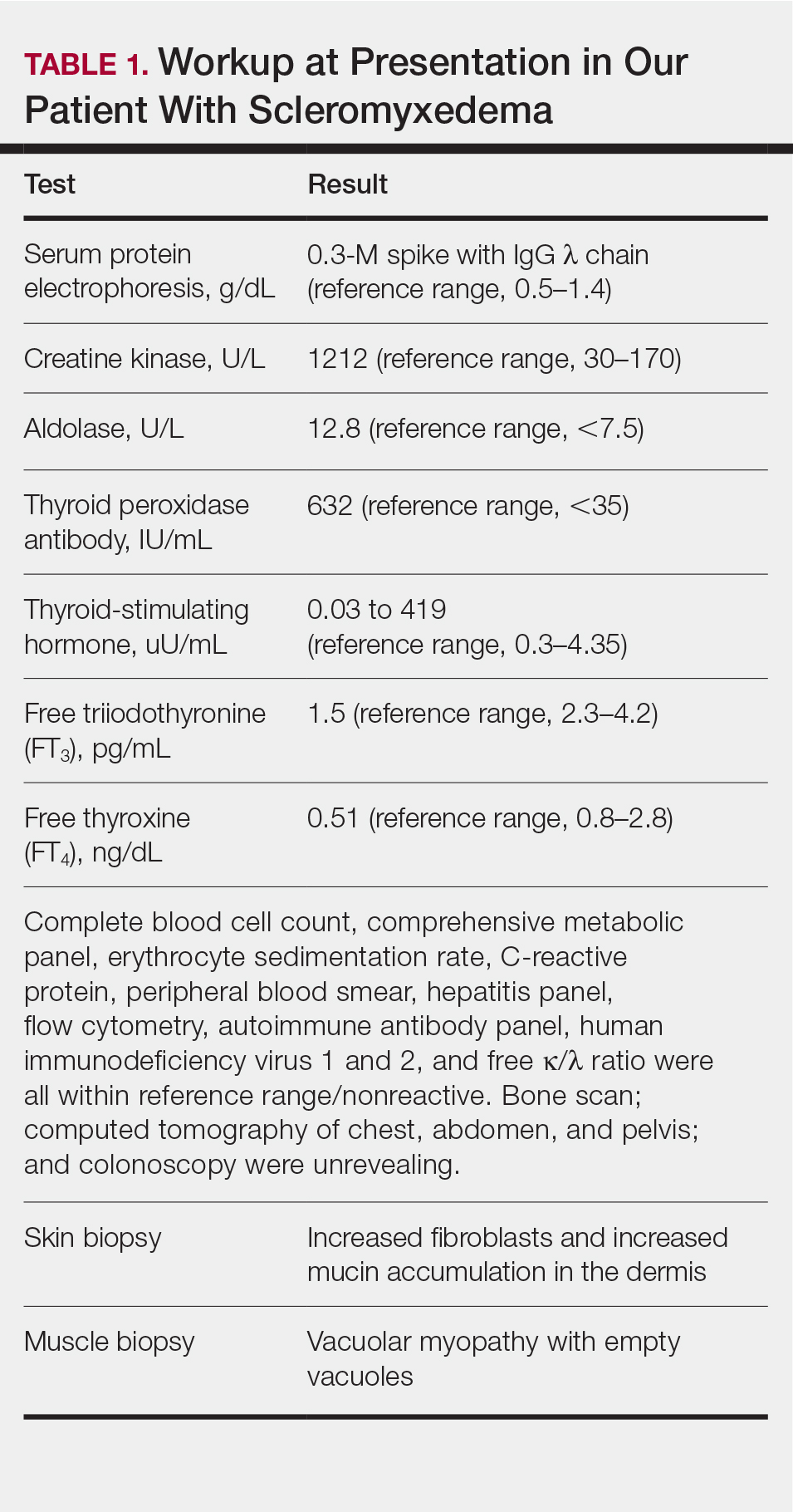
A 44-year-old woman presented with a progressive eruption of thickened skin and papules spanning many months. The papules ranged from flesh colored to erythematous and covered more than 80% of the body surface area, most notably involving the face, neck, ears, arms, chest, abdomen, and thighs (Figures 1A and 2A). Review of systems was notable for pruritus, muscle pain but no weakness, dysphagia, and constipation. Her medical history included childhood atopic dermatitis and Hashimoto thyroiditis. Hypothyroidism was diagnosed with support of a thyroid ultrasound and thyroid peroxidase antibodies. It was treated with oral levothyroxine for 2 years prior to the skin eruption. Thyroid biopsy was not performed. Her thyroid-stimulating hormone levels notably fluctuated in the year prior to presentation despite close clinical and laboratory monitoring by an endocrinologist. Laboratory results are summarized in Table 1. Both skin and muscle9 biopsies were consistent with SM (Figure 3) and are summarized in Table 1.
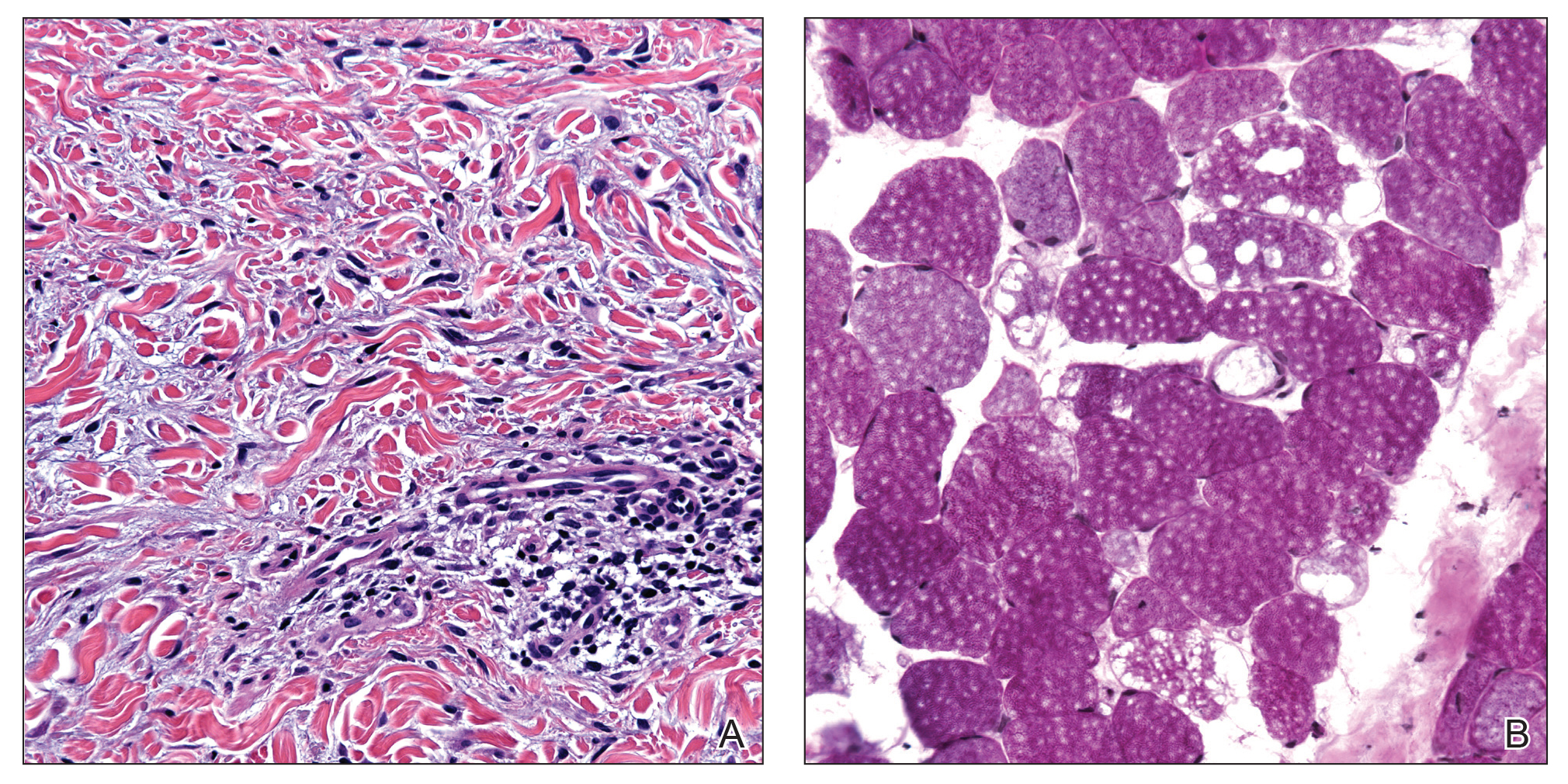
Figure 3. A, Increased number of fibroblasts and mucin deposition splayed between collagen bundles (H&E, original magnification ×400). B, Large, empty, cytoplasmic vacuoles with marked variation in muscle fiber size and paucity of inflammation and necrosis (periodic acid– Schiff, original magnification ×20).
Shortly after presentation to our clinic the patient developed acute concerns of confusion and muscle weakness. She was admitted for further inpatient management due to concern for dermato-neuro syndrome, a rare but potentially fatal decline in neurological status that can progress to coma and death, rather than myxedema coma. On admission, a thyroid function test showed subclinical hypothyroidism with a thyroid-stimulating hormone level of 6.35 uU/mL (reference range, 0.3–4.35 uU/mL) and free thyroxine (FT4) level of 1.5 ng/dL (reference range, 0.8–2.8 ng/dL). While hospitalized she was started on intravenous levothyroxine, systemic steroids, and a course of intravenous immunoglobulin (IVIg) treatment consisting of 2 g/kg divided over 5 days. On this regimen, her mental status quickly returned to baseline and other symptoms improved, including the skin eruption (Figures 1B and 2B). She has been maintained on lenalidomide 25 mg/d for the first 3 weeks of each month as well as monthly IVIg infusions. Her thyroid levels have persistently fluctuated despite intramuscular levothyroxine dosing, but her skin has remained clear with continued SM-directed therapy.