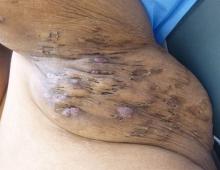
Rigorous evidence is unavailable for most interventions for treating hidradenitis suppurativa (HS), so management needs to be individualized, according to the
The guidelines were published in the Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology.
In an interview, Christopher Sayed, MD, cochair of the guidelines committee, of the department of dermatology at the University of North Carolina, Chapel Hill, said in an interview that the North American guidelines vary from the British Association of Dermatologists (Br J Dermatol. 2018 Dec 15. doi: 10.1111/bjd.17537) and European guidelines (J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol. 2015 Apr;29[4]:619-44). For example, surgery is an active treatment option for various stages of the disorder in the North American guidelines, whereas surgery is considered a last-ditch effort in the British and European guidelines.
Surgical intervention is often needed “for patients to be the best they can be, and it can be difficult for medicine alone to fix [certain] patients,” Dr. Sayed said. This point that “using medical treatment alone or just surgical treatment alone often doesn’t lead to the best outcome” is stressed in the North American guidelines, he noted.
Limited evidence for high-level recommendations
Adalimumab (Humira), a tumor necrosis factor blocker, was the only therapy for which level 1A evidence is available, and this is because of its study in large-scale randomized controlled trials. (The Food and Drug Administration approved adalimumab in 2015 for treating moderate to severe HS.) Other biologic therapies such as infliximab, anakinra, and ustekinumab carry level 2B recommendations, which Dr. Sayed said will likely influence the availability of these therapies.
Similarly, Nd:YAG laser carries a level 2B recommendation, as does wide excision surgical intervention.
Many of the other treatment modalities explored in the guidelines are not well supported by the literature, according to Dr. Sayed . “The vast majority ... had category C recommendations,” he said. “Some things we tried to evaluate that, really, we can’t give any recommendation on at all because there was no evidence.” He noted that changes in lifestyle and dietary practices are issues patients with HS frequently bring up, but they carry very little evidence of benefit in the literature.
“Even things we use very commonly in HS are often supported by weak evidence because we have to rely on clinical experience. ... There’s just not funding for trials of older drugs or lifestyle interventions,” he said. Treatment mainstays such as tetracycline-class antibiotics, for example, similarly have no large-scale randomized controlled trials to support their use.
Consider comorbidity screening
Treatment is frequently complicated by patient comorbidities, including type 2 diabetes, metabolic syndrome, polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS), and impaired sexual health, said Dr. Sayed.
“The disease leads to scarring and disfigurement, and can [have a] higher impact on quality of life than almost any other dermatologic disease if you compare them side by side using quality of life measures,” he noted. “We know these patients are more likely to have depression, there are high rates of suicide among these patients. A lot of that has to do with the fact that it’s a chronic disease where there is pain and disfigurement, and patients often grow very, very frustrated in part due to the disease.”
He advised consistent follow-up to ensure patients are not frustrated because of lack of perceived progress.