Psoriasis is a chronic, autoimmune-mediated disease estimated to affect 2.8% of the US population.1 The pathogenesis of psoriasis is thought to involve a complex process triggered by a combination of genetic and environmental factors that induce tumor necrosis factor (TNF) α secretion by keratinocytes, which in turn activates dendritic cells. Activated dendritic cells produce IL-23, leading to helper T cell (TH17) differentiation.2,3 TH17 cells secrete IL-17A, which has been shown to promote psoriatic skin changes.4 Therefore, TNF-α, IL-23, and IL-17A have been recognized as key targets for psoriasis therapy.
The newest biologic agents targeting IL-17–mediated pathways include ixekizumab, brodalumab, and bimekizumab. Secukinumab, the first US Food and Drug Administration (FDA)–approved IL-17 inhibitor, has been available since 2015 and therefore is not included in this review. IL-23 inhibitors that are FDA approved or being evaluated in clinical trials include guselkumab, tildrakizumab, and risankizumab. In addition, certolizumab pegol, a TNF-α inhibitor, is being studied for use in psoriasis.
METHODS
We reviewed the published results of phase 3 clinical trials for ixekizumab, brodalumab, bimekizumab, guselkumab, tildrakizumab, risankizumab, and certolizumab pegol. We performed an English-language literature search (January 1, 2012 to October 15, 2017) of articles indexed for PubMed/MEDLINE using the following combinations of keywords: IL-23 and psoriasis; IL-17 and psoriasis; tumor necrosis factor and psoriasis; [drug name] and psoriasis. If data from phase 3 clinical trials were not yet available, data from phase 2 clinical trials were incorporated in our analysis. We also reviewed citations within articles to identify relevant sources.
RESULTS
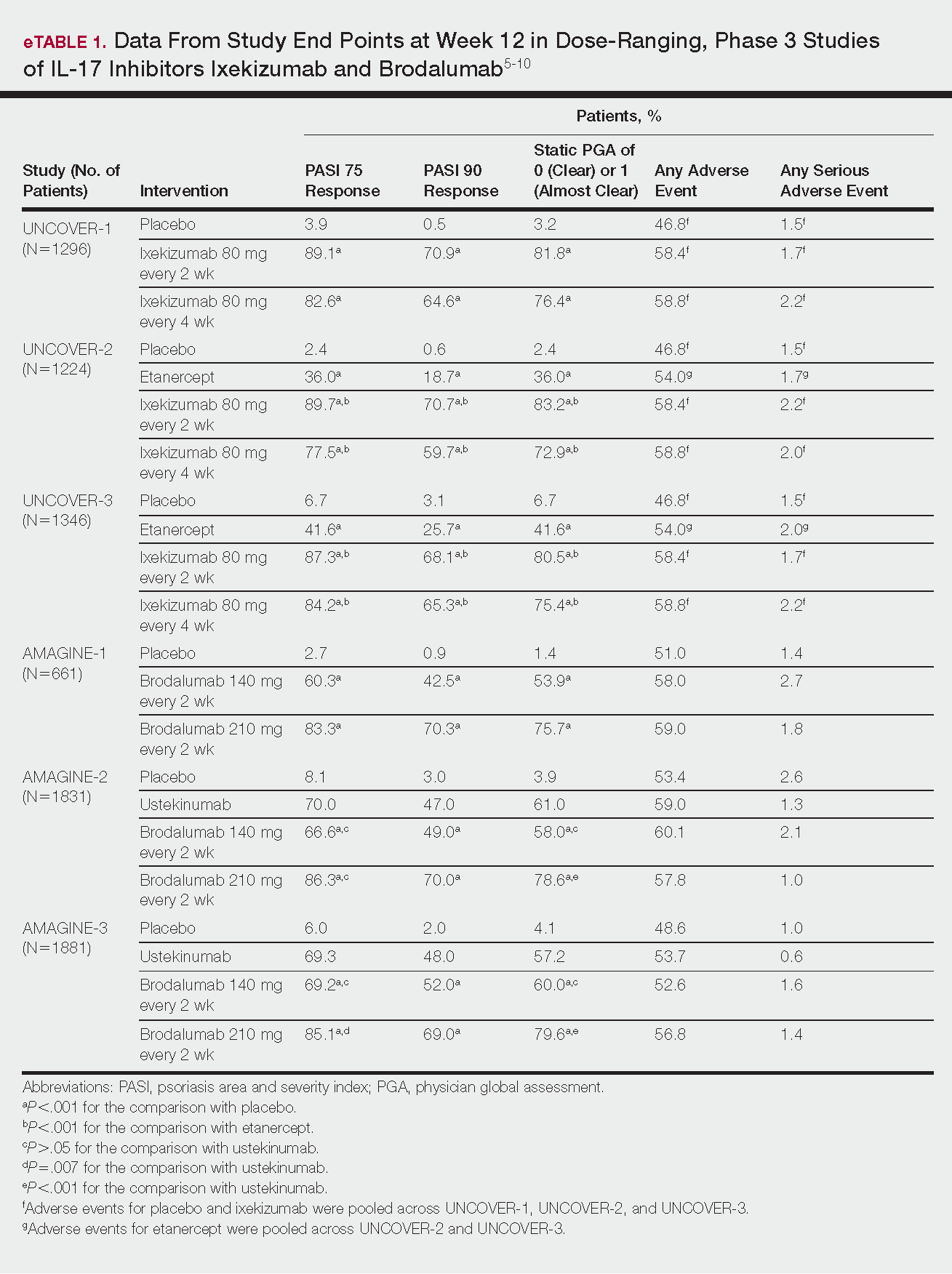
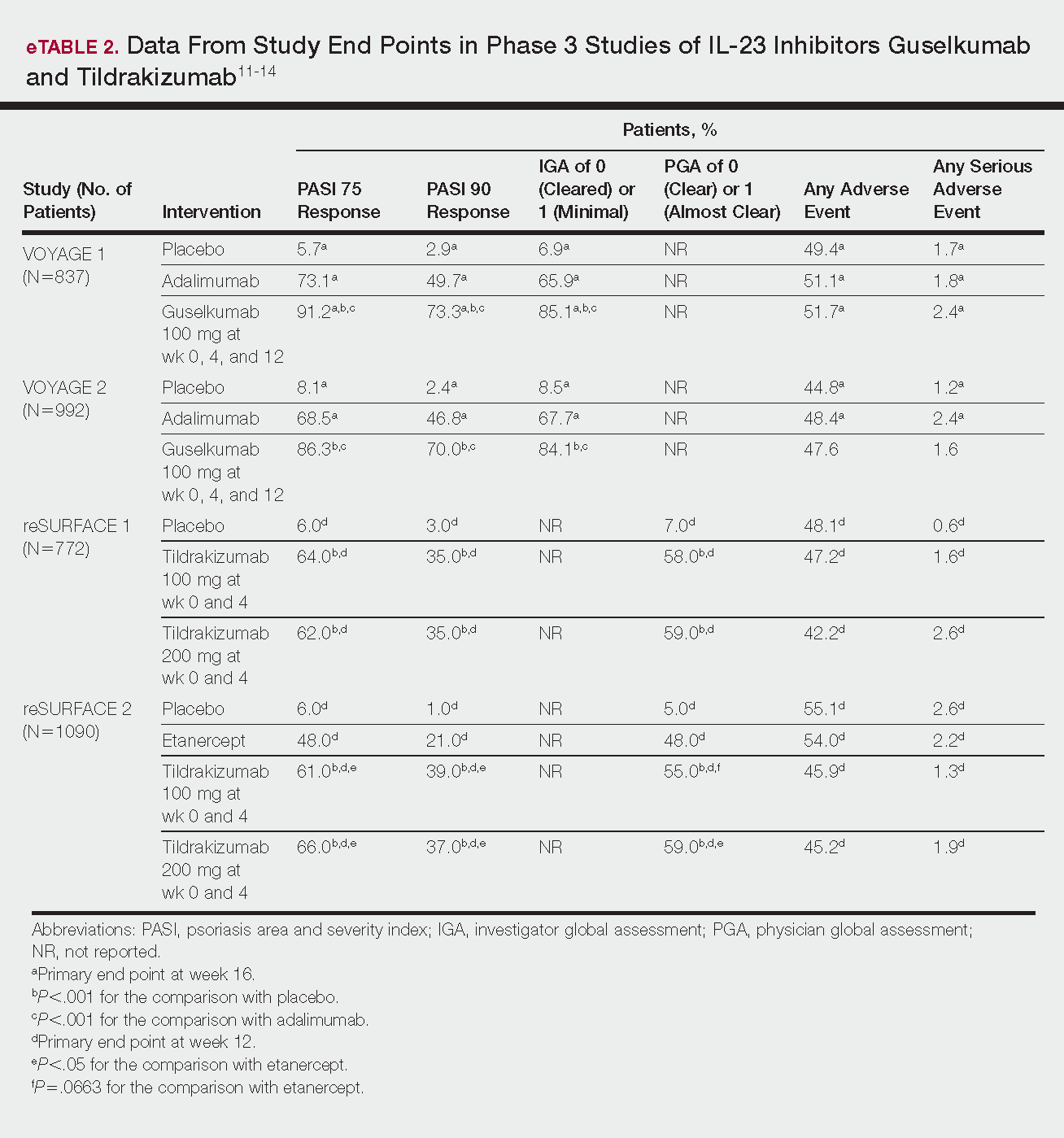
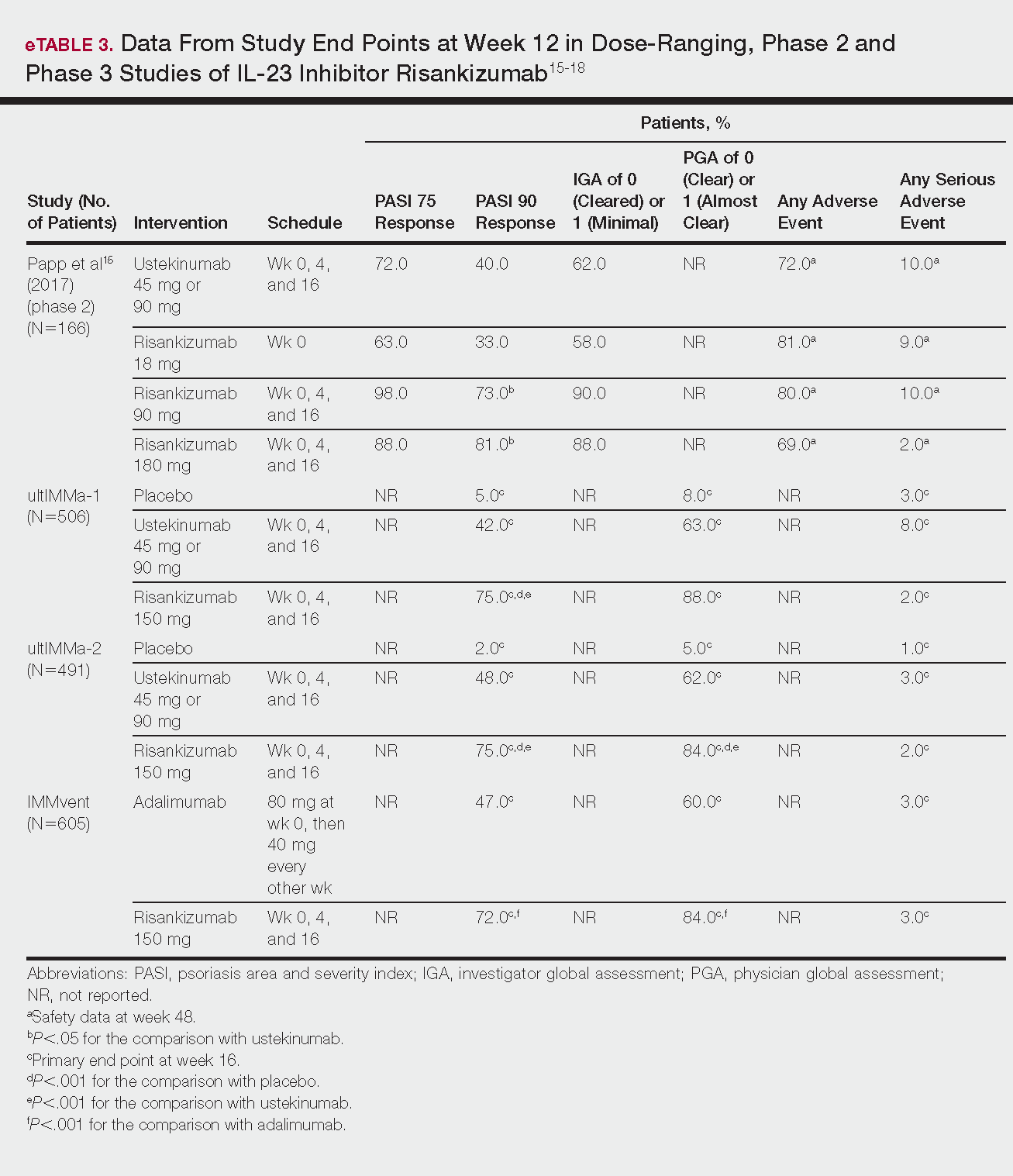
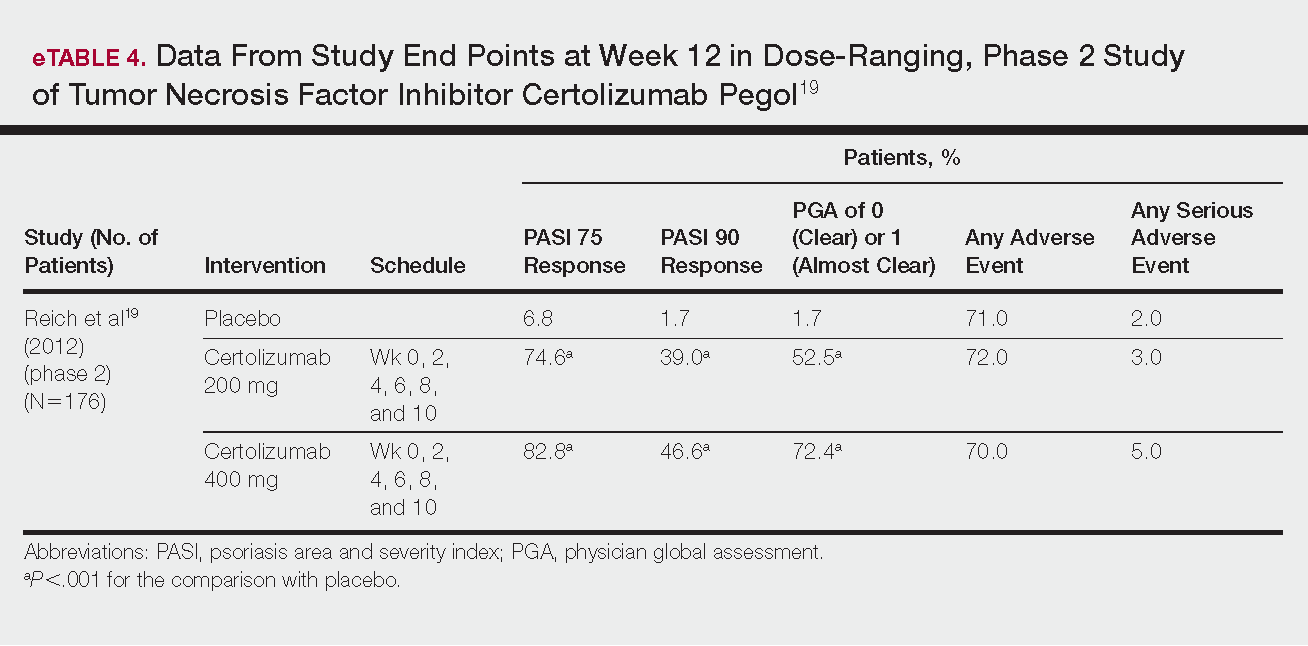
Phase 3 clinical trial design, efficacy, and adverse events (AEs) for ixekizumab and brodalumab are reported in eTable 15-10 and for guselkumab and tildrakizumab in eTable 2.11-14 Phase 2 clinical trial design, efficacy, and AEs are presented for risankizumab in eTable 315-18 and for certolizumab pegol in eTable 4.17,19 No published clinical trial data were found for bimekizumab.