Interestingly, the vesicular eruption that those investigators describe – monomorphic vesicles on the trunk and extremity – can occur in the more acute phase. That’s fascinating to me because widespread vesicular eruptions are not a thing that we commonly see. If it is not an autoimmune blistering disease, and not a drug-induced blistering process, then you’re really left with viral. Rickettsialpox can do that, as can primary varicella, disseminated herpes, disseminated zoster, and now COVID. So that’s intriguing.
I got called to see a patient yesterday who had symptoms of COVID about a month ago. She was not PCR tested at the time but she is now negative. She has a widespread eruption of tiny vesicles on an erythematous base. An IgG for COVID is positive. How do we decide whether her skin lesions have active virus in them?
The many dermatologic manifestations of COVID-19
Dr. Lipper: In the series in Spain, almost 1 out of 10 patients were found to have a widespread vesicular rash. And just under half had maculopapular exanthems. The information arising from the AAD registry will be of great interest and build on this paper.
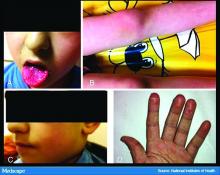
In England, the National Health Service and the Paediatric Intensive Care Society recently put out a warning about an alarming number of children with COVID-19 who developed symptoms mimicking Kawasaki disease (high fever, abdominal pain, rash, swollen lymph nodes, mucositis, and conjunctivitis). These kids have systemic inflammation and vasculitis and are critically ill. That was followed by an alert from the New York City Health Department about cases there, which as of May 6 numbered 64. Another 25 children with similar findings have been identified in France.
This is such a scary development, especially because children were supposed to be relatively “safe” from this virus. Any thoughts on who is at risk or why?
Dr. Fox: It’s very alarming. It appears that these cases look just like Kawasaki disease.
It was once hypothesized that Coronaviridae was the cause of Kawasaki disease. Then that got debunked. But these cases now raise the question of whether Kawasaki disease may be virally mediated. Is it an immune reaction to an infectious trigger? Is it actually Coronaviridae that triggers it?
As with these pernio cases, I think we’re going to learn about the pathophysiology of these diseases that we currently look at as secondary responses or immune reactions to unknown triggers. We’re going to learn a lot about them and about the immune system because of how this virus is acting on the immune system.
Dr. Lipper: As is the case with patients with pernio-like lesions, some of these children with Kawasaki-like disease are PCR negative for SARS-CoV-2. It will be interesting to see what happens with antibody testing in this population.
Dr. Fox: Agree. While some of the manufacturers of serology tests have claimed that they have very high sensitivity and specificity, that has not been my experience.
Dr. Lipper: I’ve had a number of patients with a clinical picture that strongly suggests COVID whose serology tests have been negative.
Dr. Fox: As have I. While this could be the result of faulty tests, my biggest worry is that it means that people with mild disease do not mount an antibody response. And if people who have disease can’t make antibodies, then there’s no herd immunity. If there’s no herd immunity, we’re stuck in lockdown until there’s a vaccine.
Dr. Lipper: That is a scary but real possibility. We need evidence – evidence like that provided by the AAD registry.
Dr. Fox: Agree. I look forward to sharing those results with you when we have them.
Dr. Lipper is a clinical assistant professor at the University of Vermont, Burlington, and a partner at Advanced DermCare in Danbury, Conn.
Dr. Fox is a professor in the department of dermatology at the University of California, San Francisco. She is a hospital-based dermatologist who specializes in the care of patients with complex skin conditions. She is immediate past president of the Medical Dermatology Society and current president of the Society of Dermatology Hospitalists.
This article was first published on Medscape.com.