ANSWER
The correct answer is psoriasis vulgaris (choice “a”).
DISCUSSION
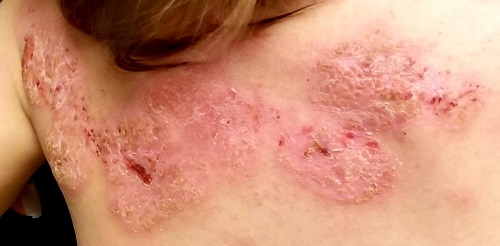
At least 30% of patients with psoriasis have a family history of the disease—a meaningful clue in developing a differential. Besides asking about the history, always look for corroborating signs in areas where the disease is commonly seen (eg, the fingernails). In this case, further corroboration was provided by the history of illness at the time of the rash’s onset; what was initially strep-driven guttate psoriasis morphed into full-blown psoriasis vulgaris.
The heavy scales, with their salmon-pink base, tipped the scales in favor of psoriasis as the diagnosis. The pinpoint bleeding (known as the Auspitz sign), although not pathognomic for psoriasis, is certainly suggestive of it.
In adults, these findings would probably have been sufficient to settle on psoriasis. But before labeling a young child with a serious, lifelong diagnosis, it was necessary to be sure. For one thing, advanced psoriasis is very unusual in children as young as this patient, and for another, treatment would likely be problematic. Fortunately for clarity’s sake, the biopsy was consistent with psoriasis and inconsistent with the other items in the differential.
TREATMENT
The patient was prescribed a topical steroid cream to apply every other day, alternating with vitamin D–derived ointment. In addition, he was advised to increase his exposure to natural sunlight. Phototherapy with narrow-band ultraviolet light B would be a superior option, but his family lives too far from the clinic to make 3 roundtrips per week for such treatment.
If these measures fail, a biologic agent may be appropriate. Unfortunately, the patient’s insurance carrier requires the failure of several other modalities before it will approve use of such therapy.