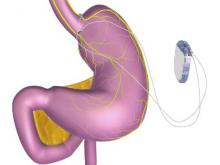
A novel implantable device that delivers electrical pulses to the intra-abdominal vagus nerve has been approved for treatment of obesity in adults, providing a less invasive alternative to bariatric surgery.
The Maestro Rechargeable System is “the first weight loss treatment device that targets the nerve pathway between the brain and the stomach that controls feelings of hunger and fullness,” according to the Food and Drug Administration statement released Jan. 14. The last device approved by the FDA for treatment of obesity was the Realize gastric band, in September 2007.
The device is approved for adults aged 18 and older with a body mass index of at least 40-45 kg/m2, or at least 35-39.9 kg/m2 with a related health condition such as high blood pressure or high cholesterol levels, who have tried to lose weight in a supervised weight management program within the past 5 years.
The system includes a rechargeable electrical pulse generator implanted into the lateral chest wall, connected to two electrical leads placed around the abdominal vagus nerve via a laparoscopic procedure. “It works by sending intermittent electrical pulses to the trunks in the abdominal vagus nerve, which is involved in regulating stomach emptying and signaling to the brain that the stomach feels empty or full,” the FDA statement said, adding: “Although it is known that the electric stimulation blocks nerve activity between the brain and the stomach, the specific mechanisms for weight loss due to use of the device are unknown.”
The manufacturer, EnteroMedics, refers to the treatment as “VBLOC therapy,” delivered by the Maestro System. The company expects that the device will be available this year “on a limited basis” at select Bariatric Centers of Excellence in the United States, according to a statement issued by EnteroMedics on Jan. 14.
FDA approval was based on the results of the ReCharge study of 233 patients with a body mass index of at least 35 kg/m2; the device was activated in 157 patients, and the remaining patients had the device implanted but it was not activated and they served as controls.
After 12 months, those with the activated device lost 8.5% more excess weight than did the controls. Among those who had the device activated, almost 53% lost at least 20% of their excess weight and 38% lost at least 35% of their excess weight, according to the FDA.
The study did not meet the primary effectiveness endpoint, which was that those on active treatment would lose at least 10% more excess weight than would the controls. However, the majority of an FDA advisory panel that reviewed the data at a meeting in June 2014 supported approval, agreeing that the benefits outweighed the risks for the proposed indication. Panelists cited the fact that the study safety endpoint was met and that the device was effective in helping some people lose weight.
The FDA statement said the decision to approve the device was based on the panel’s recommendation, the study results, and an FDA survey of patient preferences for obesity devices, which found that “a group of patients would accept risks associated with this surgically implanted device for the amounts of weight loss expected to be provided by the device.”
As a condition for approval, EnteroMedics is required to conduct a 5-year postmarketing study that will collect safety and effectiveness data in at least 100 patients, including weight loss, adverse events, surgical revisions and explants and changes in obesity-related comorbidities, according to the FDA.
Serious adverse events in the ReCharge study were nausea, pain at the neuroregulator site, vomiting, and surgical complications; other adverse events were heartburn, problems swallowing, belching, mild nausea, and chest pain, the FDA noted.
The EnteroMedics statement says that contraindications for VBLOC therapy include liver cirrhosis, portal hypertension, esophageal varices or an uncorrectable, clinically significant hiatal hernia; patients for whom magnetic resonance imaging or diathermy use is planned; patients at high risk for surgical complications; and patients who have permanently implanted, electrically-powered medical devices or gastrointestinal devices or prostheses, such as pacemakers, implanted defibrillators, or neurostimulators.