Starting in 2016, the Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services began paying physicians for advance care planning discussions with the approval of two new codes: 99497 and 99498. The codes pay about $86 for the first 30 minutes of a face-to-face conversation with a patient, family member, and/or surrogate and about $75 for additional sessions. Services can be furnished in both inpatient and ambulatory settings, and payment is not limited to particular physician specialties.
In 2016, health care professionals in New England (Connecticut, Maine, Massachusetts, New Hampshire, Rhode Island, and Vermont) billed Medicare 26,522 times for the advance care planning (ACP) codes for a total of 24,536 patients, which represented less than 1% of Medicare beneficiaries in New England at the time, according to Kimberly Pelland, MPH, of Healthcentric Advisors, Providence, R.I., and her colleagues. Most claims were billed in the office, followed by in nursing homes, and in hospitals; 40% of conversations occurred during an annual wellness visit (JAMA Intern Med. 2019 March 11. doi:10.1001/jamainternmed.2018.8107).
Internists billed Medicare the most for ACP claims (65%), followed by family physicians (22%) gerontologists (5%), and oncologist/hematologists (0.3%), according to the analysis based on 2016 Medicare claims data and Census Bureau data. A greater proportion of patients with ACP claims were female, aged 85 years or older, enrolled in hospice, and died in the study year. Patients had higher odds of having an ACP claim if they were older and had lower income, and if they had cancer, heart failure, stroke, chronic kidney disease, or dementia. Male patients who were Asian, black, and Hispanic had lower chances of having an ACP claim.
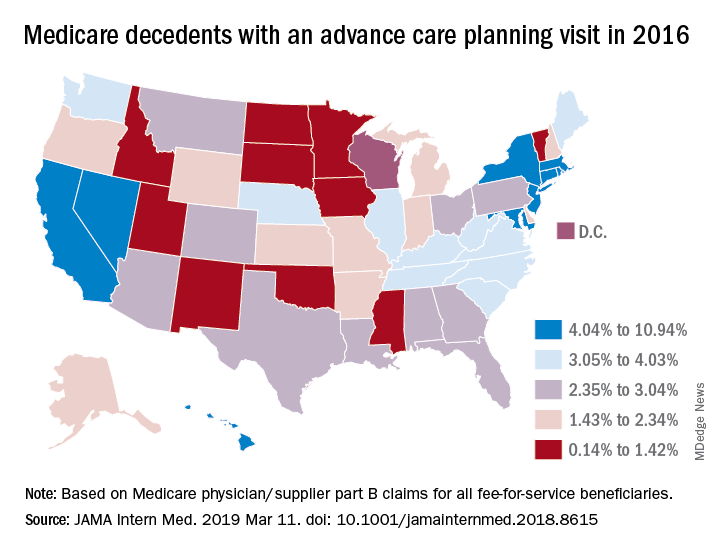
In a related study, Emmanuelle Belanger, PhD, of Brown University, Providence, R.I., and her colleagues examined national Medicare data from 2016 to the third quarter of 2017. Across the United States, 2% of Medicare patients aged 65 years and older received advance care planning services that were billed under the ACP codes (JAMA Intern Med. 2019 March 11. doi: 10.1001/jamainternmed.2018.8615). Visits billed under the ACP codes increased from 538,275 to 633,214 during the same time period. Claim rates were higher among patients who died within the study period, reaching 3% in 2016 and 6% in 2017. The percentage of decedents with an ACP billed visit varied strongly across states, with states such as North Dakota, South Dakota, and Wyoming having the fewest ACP visits billed and states such as California and Nevada having the most. ACP billed visits increased in all settings in 2017, but primarily in hospitals and nursing homes. Nationally, internists billed the codes most (48%), followed by family physicians (28%).
While the two studies indicate low usage of the ACP codes, many physicians are discussing advance care planning with their patients, said Mary M. Newman, MD, an internist based in Lutherville, Md., and former American College of Physicians adviser to the American Medical Association Relative Scale Value Update Committee (RUC).
“What cannot be captured by tracking under Medicare claims data are those shorter conversations that we have frequently,” Dr. Newman said in an interview. “If we have a short conversation about advance care planning, it gets folded into our evaluation and management visit. It’s not going to be separately billed.”
At the same time, some patients are not ready to discuss end-of-life options and decline the discussions when asked, Dr. Newman said. Particularly for healthier patients, end of life care is not a primary focus, she noted.
“Not everybody’s ready to have an advance care planning [discussion] that lasts 16-45 minutes,” she said. “Many people over age 65 are not ready to deal with advance care planning in their day-to-day lives, and it may not be what they wish to discuss. I offer the option to patients and some say, ‘Yes, I’d love to,’ and others decline or postpone.”
Low usage of the ACP codes may be associated with lack of awareness, uncertainty about appropriate code use, or associated billing that is not part of the standard workflow, Ankita Mehta, MD, of Mount Sinai in New York wrote an editorial accompanying the studies (JAMA Intern Med. 2019 March 11. doi:10.1001/jamainternmed.2018.8105).
“Regardless, the low rates of utilization of ACP codes is alarming and highlights the need to create strategies to integrate ACP discussions into standard practice and build ACP documentation and billing in clinical workflow,” Dr. Mehta said.
Dr. Newman agreed that more education among physicians is needed.
“The amount of education clinicians have received varies tremendously across the geography of the country,” she said. “I think the codes are going to be slowly adopted. The challenge to us is to make sure we’re all better educated on palliative care as people age and get sick and that we are sensitive to our patients explicit and implicit needs for these discussions.”